Benzene and those cyclic compounds that chemically behave as benzene are called aromatic compounds. Eg.

Aromatic compounds are also known as arenes (i.e. aromatic alkenes).
{ the term aromatic was derived from the Greek word ‘aroma’ meaning sweet smelling}
Kekule, a German scientist proposed the structure of benzene for the first time. According to Kekule, all the 6 carbon atoms of benzene molecule are joint to each other by alternate single and double bond forming a hexagonal ring and a hydrogen atom is bonded to each carbon atom.

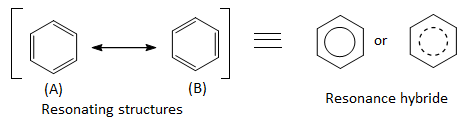
The double bonds may be localized in any position and therefore following resonating structures are possible :

According to these structures, there should be three single bonds (bond length 154 pm) and three double bonds (bond length 134 pm) between carbon atoms in the benzene molecule. But actually it has been found by X- ray diffraction studies that all the carbon-carbon bonds in benzene are equivalent and have bond length 139 pm , which is intermediate between C – C (154 pm) and C = C (134 pm). Thus, the actual structure of benzene is different from both ‘A’ and ‘B’ and is a resonance hybrid of these two resonating forms.
{ Note: pm = picometre, 1pm = 10 -12 m}